MySQL优化
1 | |
一、SQL优化
SQL优化的目的是为了SQL语句能够具备优秀的查询性能,实现这样的目的有很多的途径:
- 工程优化如何实现:数据库标准、表的结构标准、字段的标准、创建索引
- SQL语句的优化:当前SQL语句有没有命中索引。
1.工程优化如何实现
参考《MySQL军规升级版》
2.Explain执行计划——SQL优化神器
得知道当前系统里有哪些SQL是慢SQL,查询性能超过1s的sql,然后再通过Explain工具可以对当前SQL语句的性能进行判断——为什么慢,怎么解决。
要想知道哪些SQL是慢SQL,有两种方式,一种是开启本地MySQL的慢查询日志;另一种是阿里云提供的RDS(第三方部署的MySQL服务器),提供了查询慢SQL的功能。
1 | |
通过在SQL语句前面加上explain关键字,执行后并不会真正的执行sql语句本身,而是通过explain工具来分析当前这条SQL语句的性能细节:比如是什么样的查询类型、可能用到的索引及实际用到的索引,和一些额外的信息。

3.MySQL的内部优化器
在SQL查询开始之前,MySQL内部优化器会进行一次自我优化,让这一次的查询性能尽可能的好。
当前执行的SQL
1 | |
内部优化器优化后的效果:
1 | |
4.select_type列
关闭 MySQL 对衍生表的合并优化:
1 | |
执行了这样的计划:
1 | |
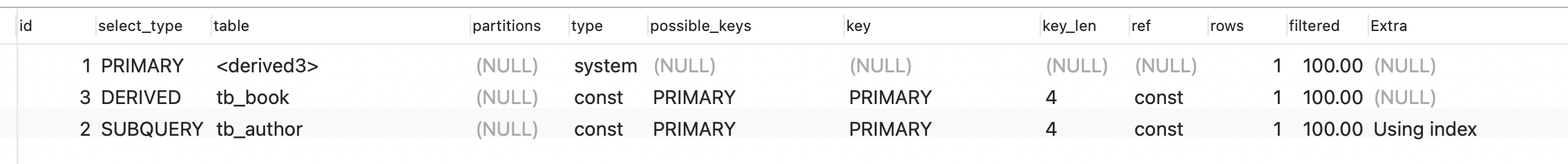
- derived:
第一条执行的sql是from后面的子查询,该子查询只要在from后面,就会生成一张衍生表,因此他的查询类型:derived
- subquery:
在select之后 from之前的子查询
- primary:
最外部的select
- simple:
不包含子查询的简单的查询
- union:
使用union进行的联合查询的类型
5.table列
当前查询正在查哪张表
6.type列
type列可以直观的判断出当前的sql语句的性能。type里的取值和性能的优劣顺序如下:
1 | |
对于SQL优化来说,要尽量保证type列的值是属于range及以上级别。
- null
性能最好的,一般在使用了聚合函数操作索引列,结果直接从索引树获取即可,因此是性能最好。
- system
很少见。直接和一条记录进行匹配。
- const
使用主键索引或唯一索引和常量进行比较,这种性能非常好
- eq_ref
在进行多表连接查询时。如果查询条件是使用了主键进行比较,那么当前查询类型是eq_ref
1 | |
ref
- 简单查询:EXPLAIN select * from tb_book where name=’book1’
如果查询条件是普通列索引,那么类型ref
- 复杂查询:EXPLAIN select book_id from tb_book left join tb_book_author on tb_book.id = tb_book_author.book_id
如果查询条件是普通列索引,那么类型ref
range:
使用索引进行范围查找
1 | |
- index
查询没有进行条件判断。但是所有的数据都可以直接从索引树上获取(book表中的所有列都有索引)
1 | |
- all
没有走索引,进行了全表扫描
1 | |
7.id列
在多个select中,id越大越先执行,如果id相同。上面的先执行。
8.possible keys列
这一次的查询可能会用到的索引。也就是说mysql内部优化器会进行判断,如果这一次查询走索引的性能比全表扫描的性能要查,那么内部优化器就让此次查询进行全表扫描——这样的判断依据我们可以通过trace工具来查看
1 | |
这条sql走索引查询的行数是500多万,那么总的数据行数也就500多万,因此直接进行全表扫描性能更快

9.key列
实际该sql语句使用的索引
10.rows列
该sql语句可能要查询的数据条数
11.key_len列
键的长度,通过这一列可以让我们知道当前命中了联合索引中的哪几列。
1 | |
name长度是74,也就是当看到key-len是74,表示使用了联合索引中的name列
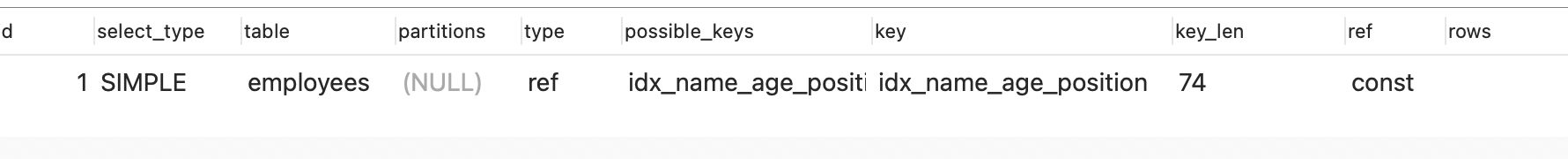
计算规则:
1 | |
12.extra列
extra列提供了额外的信息,是能够帮助我们判断当前sql的是否使用了覆盖索引、文件排序、使用了索引进行查询条件等等的信息。
Using index:使用了覆盖索引
所谓的覆盖索引,指的是当前查询的所有数据字段都是索引列,这就意味着可以直接从索引列中获取数据,而不需要进行查表。
使用覆盖索引进行性能优化这种手段是之后sql优化经常要用到的。
1 | |
using where
使用了普通索引列做查询条件
1 | |
- using index condition
查询结果没有使用覆盖索引,建议可以使用覆盖索引来优化
1 | |
- Using temporary
在非索引列上进行去重操作就需要使用一张临时表来实现,性能是非常差的。当前name列没有索引
1 | |
- Using filesort
使用文件排序: 会使用磁盘+内存的方式进行文件排序,会涉及到两个概念:单路排序、双路排序
1 | |
- Select tables optimized away
直接在索引列上进行聚合函数的操作,没有进行任何的表的操作
1 | |
13.应用场景总结
符合最左前缀法制
不能在索引上做计算、函数、类型转换,不然会变成全表扫描,如果是对日期查找,尽量通过范围查找进行优化
尽量使用覆盖索引
使用了不等于(!= 或者 <>)会导致全表扫描
使用
is null、is not null会导致全表扫描,所以尽量让属性非空使用
like以通配符开头('%abc...')会导致全表扫描字符串不加单引号会导致全表扫描
少用
or或in,MySQL 内部优化器可能会不走索引范围查询优化
1
2
3
4
5
6比如在 age >= 1 and age <= 2000000 的情况下
可以在应用层优化为多线程执行,可采用工具类 CountDownLatch
age >= 1 and age <= 1000
age >= 1001 and age <= 2000
age >= 3001 and age <= 3000
······
二、Trace工具
在执行计划中我们发现有的sql会走索引,有的sql即使明确使用了索引也不会走索引。这是因为mysql的内部优化器任务走索引的性能比不走索引全表扫描的性能要差,因此mysql内部优化器选择了使用全表扫描。依据来自于trace工具的结论。
1 | |
1 | |
三、SQL优化实战
1.order by优化
在排序应用场景中,很容易出现文件排序的问题,文件排序会对性能造成影响,因此需要优化
1 | |
优化手段:
- 如果排序的字段创建了联合索引,那么尽量在业务不冲突的情况下,遵循最左前缀法则来写排序语句。
- 如果文件排序没办法避免,那么尽量想办法使用覆盖索引。all->index
2.group by优化
group by 的原理是先排序后分组,因此对于group by 的优化参考order by
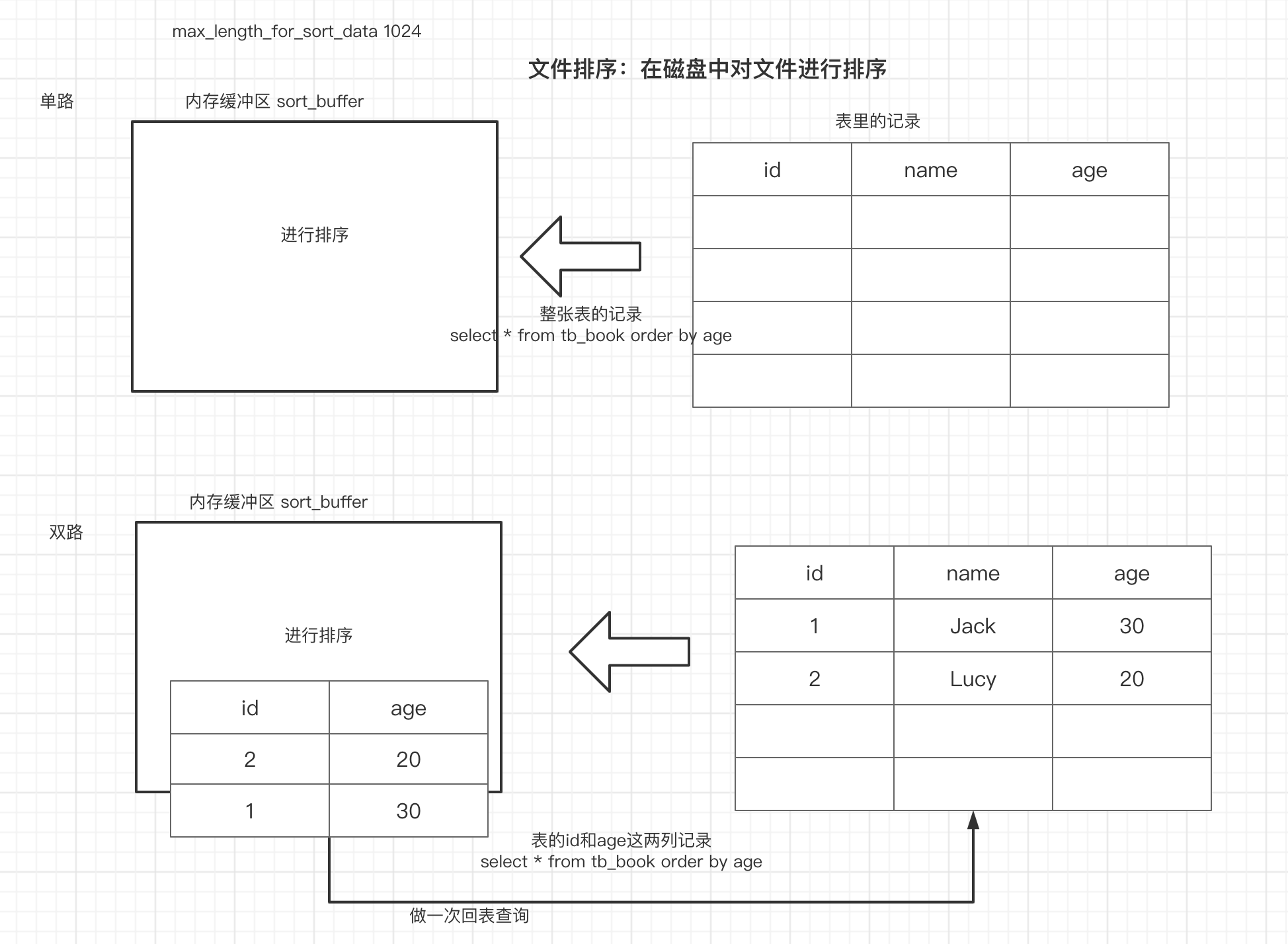
3.文件排序的原理
在执行文件排序的时候,会把查询的数据的大小与系统变量:max_length_for_sort_data的大小进行比较(默认是1024字节),如果比系统变量小,那么执行单路排序,反之则执行双路排序
- 单路排序
把所有的数据扔到sort_buffer内存缓冲区中,进行排序,然后结束
双路排序
取数据的排序字段和主键字段,在内存缓冲区中排序完成后,将主键字段做一次回表查询,获取完整数据。
4.分页优化
对于这样的优化查询,mysql会把全部的10010数据拿到,并舍弃掉前面的10000条
1 | |
如果在主键连续的情况下,可以使用主键来做条件,但是这种情况是很少见的
1 | |
对于主键不连续情况下的例子:
1 | |
5.join优化
在join中会涉及到大表(数据量大)和小表(数据量小)的概念。MySQL内部优化器会根据关联字段是否创建了索引来使用不同的算法:
Nlj(嵌套循环算法):如果关联字段使用了索引,mysql会对小表做全表扫描,用小表的数据去和大表的数据去做索引字段的关联查询(type:ref)
bnlj(块嵌套循环算法):如果关联字段没有使用索引,mysql会提供一个join buffer缓冲区,先把小表放到缓冲区中,然后全表扫描大表,把大表的数据和缓冲区中的小表数据在内存中进行匹配。
结论:使用join查询时,一定要建立关联字段的索引,且两张表的关联字段在设计之初就要做到字段类型、长度是一致的,否则索引失效。
6.in和exists优化
在sql中如果A表是大表,B表是小表,那么使用in会更加合适。反之应该使用exists。
- in: B的数据量<A的数据量
1 | |
- exists: B的数据量>A的数据量 (10: id 1. 2. 3. 4)
1 | |
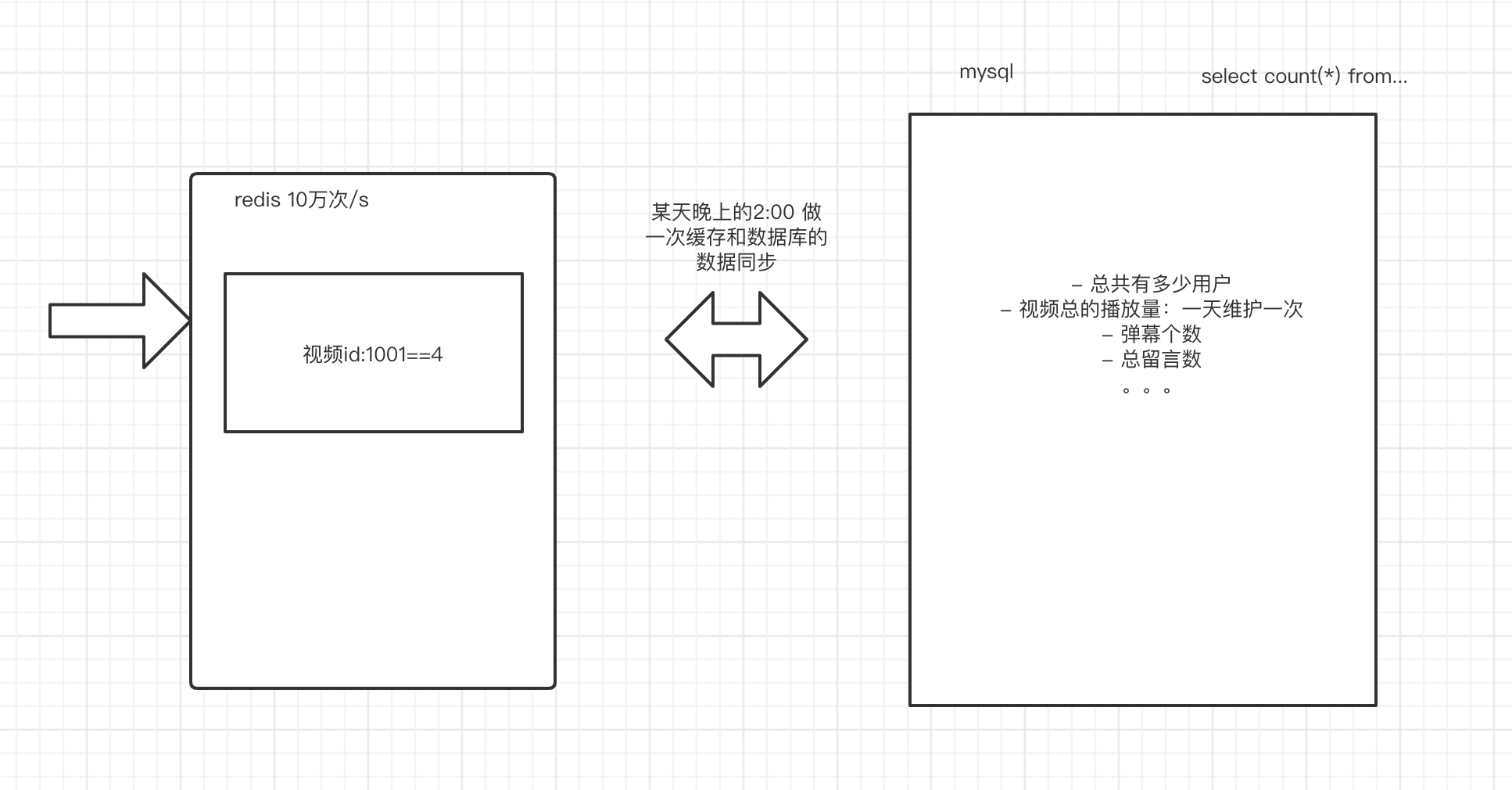
7.count优化
对于count的优化应该是架构层面的优化,因为count的统计是在一个产品会经常出现,而且每个用户访问,所以对于访问频率过高的数据建议维护在缓存中。
四、锁的定义和分类
1.锁的定义
锁是用来解决多个任务(线程、进程)在并发访问同一共享资源时带来的数据安全问题。虽然使用锁解决了数据安全问题,但是会带来性能的影响,频繁使用锁的程序的性能是必然很差的。
对于数据管理软件MySQL来说,必然会到任务的并发访问。那么MySQL是怎么样在数据安全和性能上做权衡的呢?——MVCC设计思想。
2.锁的分类
1)从性能上划分:乐观锁和悲观锁
- 悲观锁:悲观的认为当前的并发是非常严重的,所以在任何时候操作都是互斥。保证了线程的安全,但牺牲了并发性。——总有刁民要害朕。
- 乐观锁:乐观的认为当前的并发并不严重,因此对于读的情况,大家都可以进行,但是对于写的情况,再进行上锁。以CAS自旋锁,在某种情况下性能是ok的,但是频繁自旋会消耗很大的资源。——天网恢恢疏而不漏
2)从数据的操作细粒度上划分:表锁和行锁
- 表锁:对整张表上锁
- 行锁:对表中的某一行上锁。
3)从数据库的操作类型上划分:读锁和写锁
这两种锁都是属于悲观锁
- 读锁(共享锁):对于同一行数据进行”读“来说,是可以同时进行但是写不行。
- 写锁(拍他锁):在上了写锁之后,及释放写锁之前,在整个过程中是不能进行任何的其他并发操作(其他任务的读和写是都不能进行的)。
3.表锁
对整张表进行上锁。MyISAM存储引擎是天然支持表锁的,也就是说在MyISAM的存储引擎的表中如果出现并发的情况,将会出现表锁的效果。MyISAM不支持事务。InnoDB支持事务
在InnoDB中上一下表锁:
1 | |
读锁: 其他任务可以进行读,但是不能进行写
写锁:其他任务不能进行读和写。
4.行锁
MyISAM只支持表锁,但不支持行锁,InnoDB可以支持行锁。
在并发事务里,每个事务的增删改的操作相当于是上了行锁。
上行锁的方式:
- update tb_book set name=’qfjava2101’ where id=8; 对id是8的这行数据上了行锁。
- select * from tb_book where id=5 for update; 对id是5的这行数据上了行锁。
五、MVCC设计思想
MySQL为了权衡数据安全和性能,使用了MVCC多版本并发控制的设计。
1.事务的特性
- 原子性:一个事务是一个最小的操作单位(原子),多条sql语句在一个事务中要么同时成功,要么同时失败。
- 一致性:事务提交之前和回滚之后的数据是一致的。
- 持久性:事务一旦提交,对数据的影响是持久的。
- 隔离性:多个事务在并发访问下,提供了一套隔离机制,不同的隔离级别会有不同的并发效果。
2.事务的隔离级别
- read uncommitted(读未提交): 在一个事务中读取到另一个事务还没有提交的数据——脏读。
- Read committed(读已提交): 已经解决了脏读问题,在一个事务中只会读取另一个事务已提交的数据,这种情况会出现不可重复读的问题。就是:在事务中重复读数据,数据的内容是不一样的。
- repeatable read(可重复读):在一个事务中每次读取的数据都是一致的,不会出现脏读和不可重复读的问题。会出现虚读(幻读)的问题。
什么是幻读:
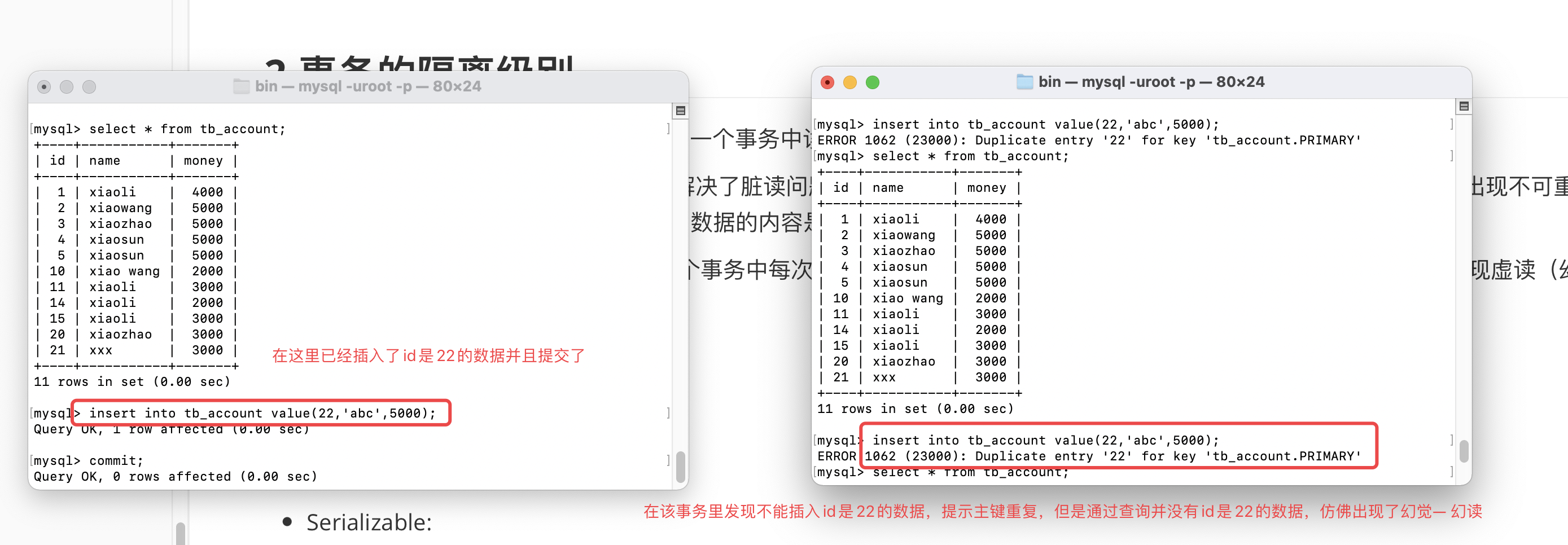
解决方案:
通过上行锁来解决虚读问题:
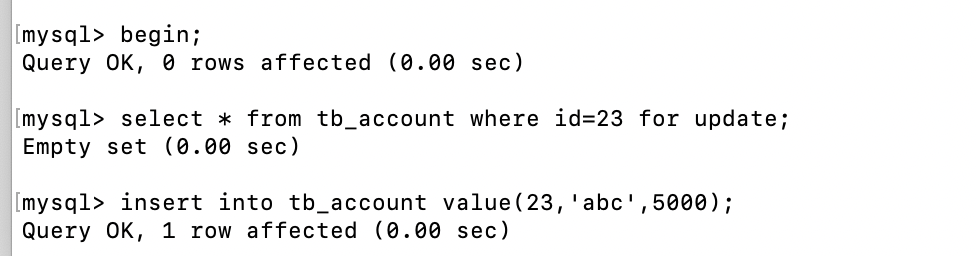
- Serializable:串行化的隔离界别直接不允许事务的并发发生,不存在任何的并发性。相当于锁表,性能非常差,一般都不考虑
脏读、不可重复读、虚读(幻读)
3.MVCC思想解读
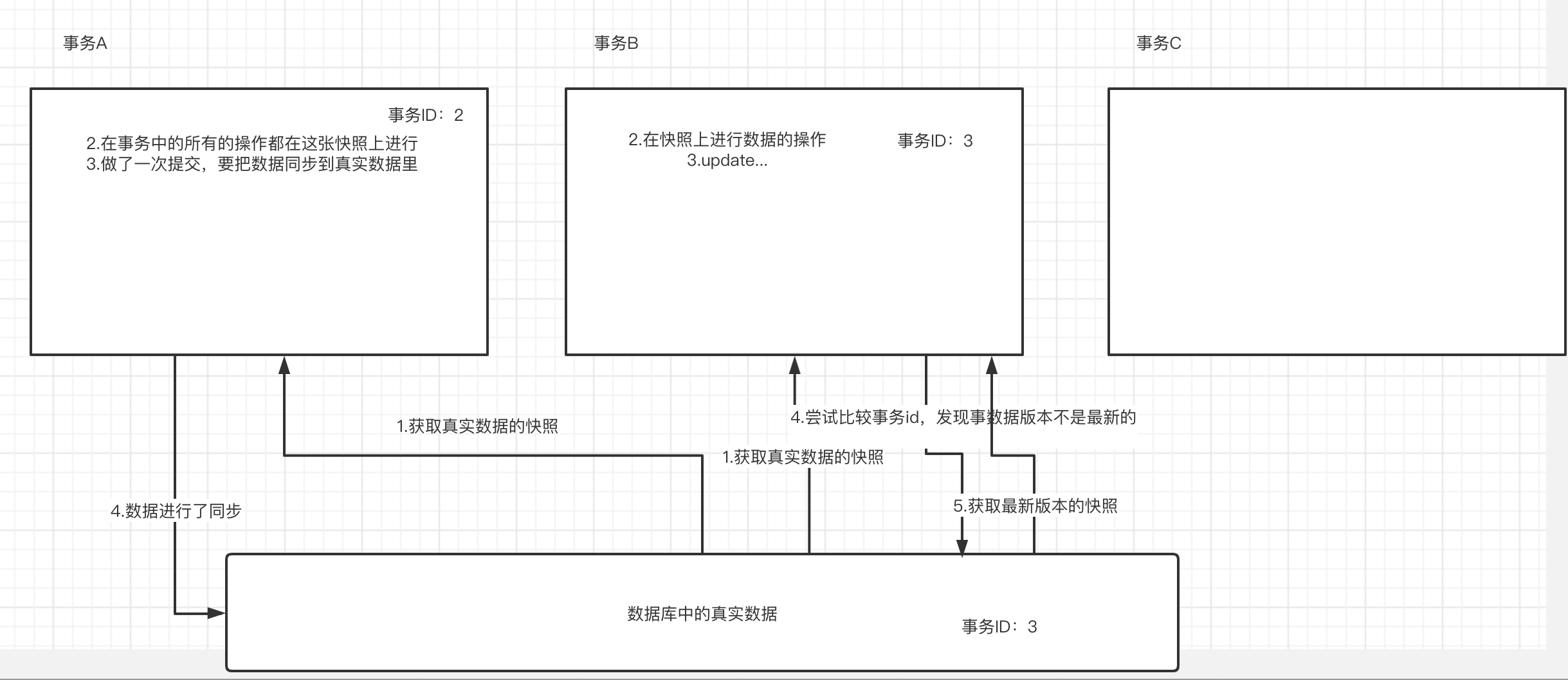
MySQL在读和写的操作中,对读的性能做了并发性的保障,让所有的读都是快照读,对于写的时候,进行版本控制,如果真实数据的版本比快照版本要新,那么写之前就要进行版本(快照)更新,这样就可以既能够提高读的并发性,又能够保证写的数据安全。
六、死锁和间隙锁
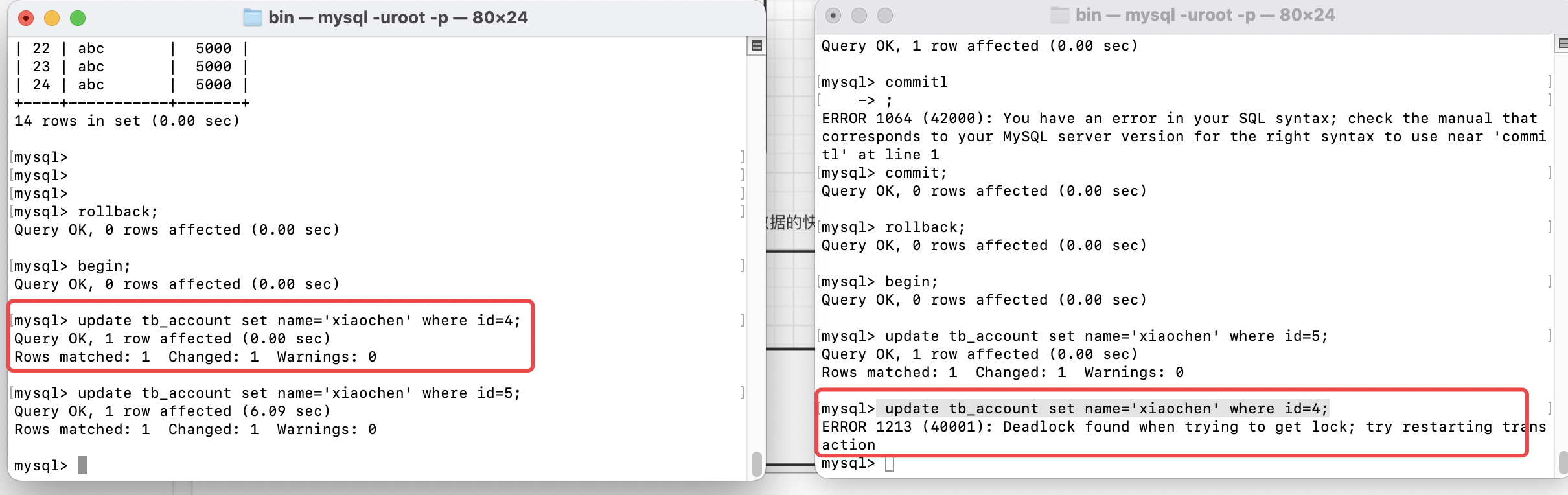
1.死锁
所谓的死锁,就是开启的锁没有办法关闭,导致资源的访问因为无法获得锁而处于阻塞状态。
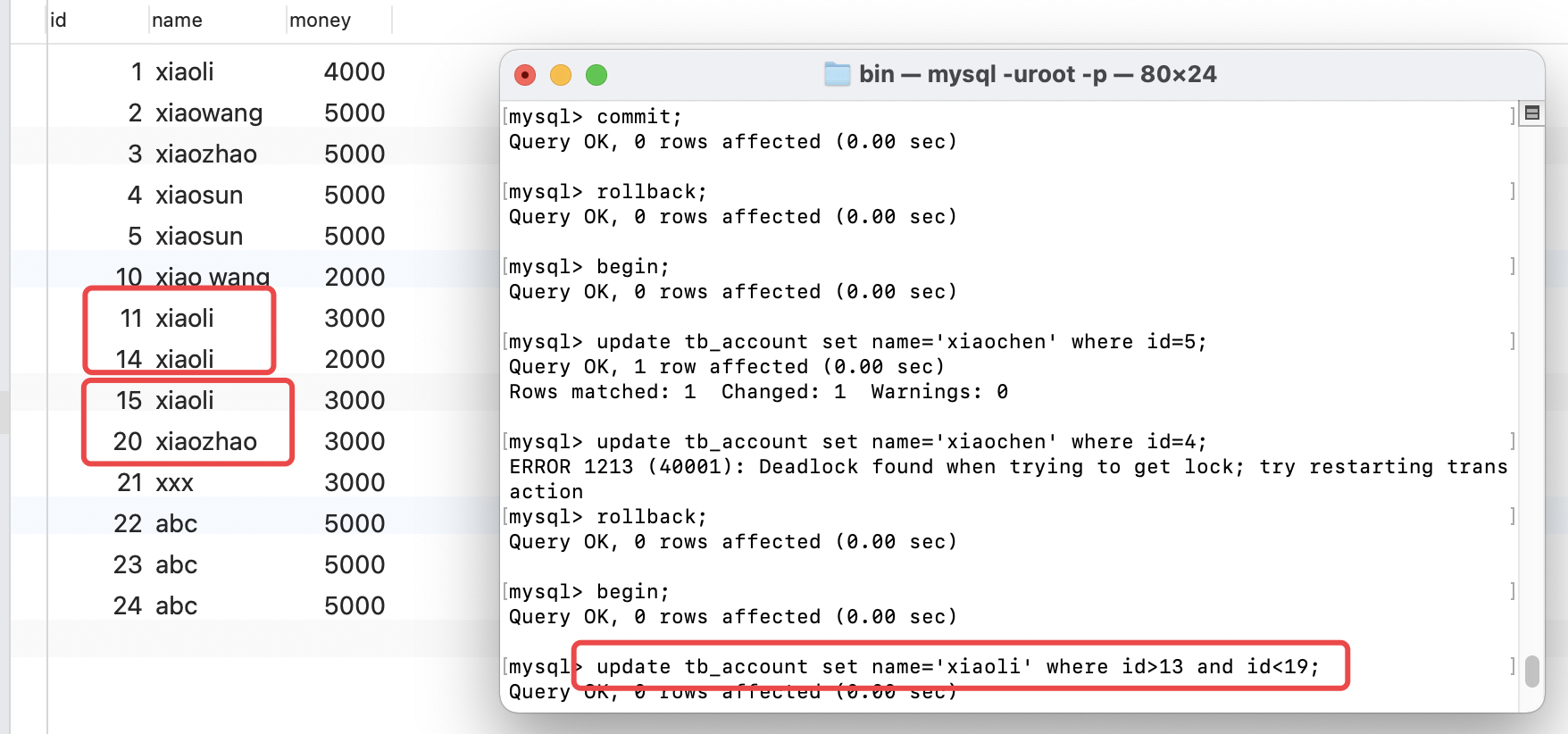
演示:事务A和事物B相互持有对方需要的锁而不释放,造成死锁的情况。
2.间隙锁
行锁只能对某一行上锁,如果相对某一个范围上锁,就可以使用间隙锁。间隙锁给的条件where id>13 and id<19,会对13 和19 所处的间隙进行上锁。
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!